Drying Rivers, Dying Livelihoods: The Crisis Threatening Rwanda’s Rivers and Communities
Drying Rivers, Dying Livelihoods: The Crisis Threatening Rwanda’s Rivers and Communities
Rwanda in different time is facing a significant environmental challenge; some of its rivers are getting smaller and drying up. This crisis is not only affecting local ecosystems but also affect environment and life of the community that depend on these vital water sources.
Rwanda, known for its stunning landscapes and many natural resources, in different time is facing a severe environmental crisis as some of its rivers are drying up and getting smaller. This growing problem threatens communities, agriculture, and biodiversity, raising concerns among scientists, environmental activists, and local residents.
As water levels continue to drop, people who depend on these rivers for their daily lives say that they struggling especial during the strong sunlight season. But what is causing the rivers to dry up? What are the effects, and what can be done to stop this disaster?

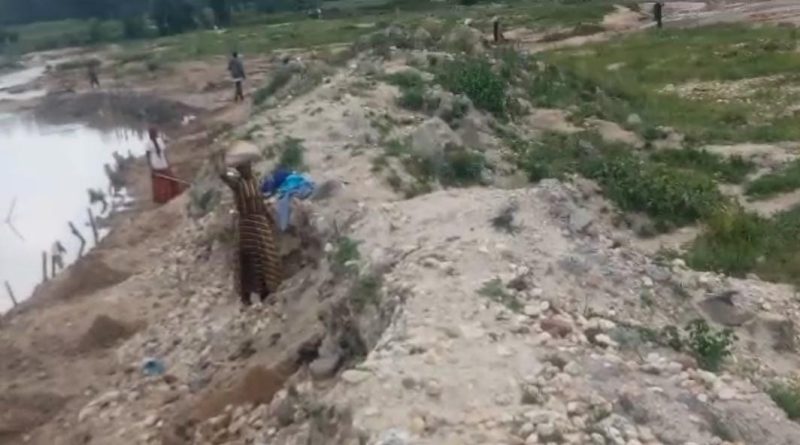
Rivers in Crisis
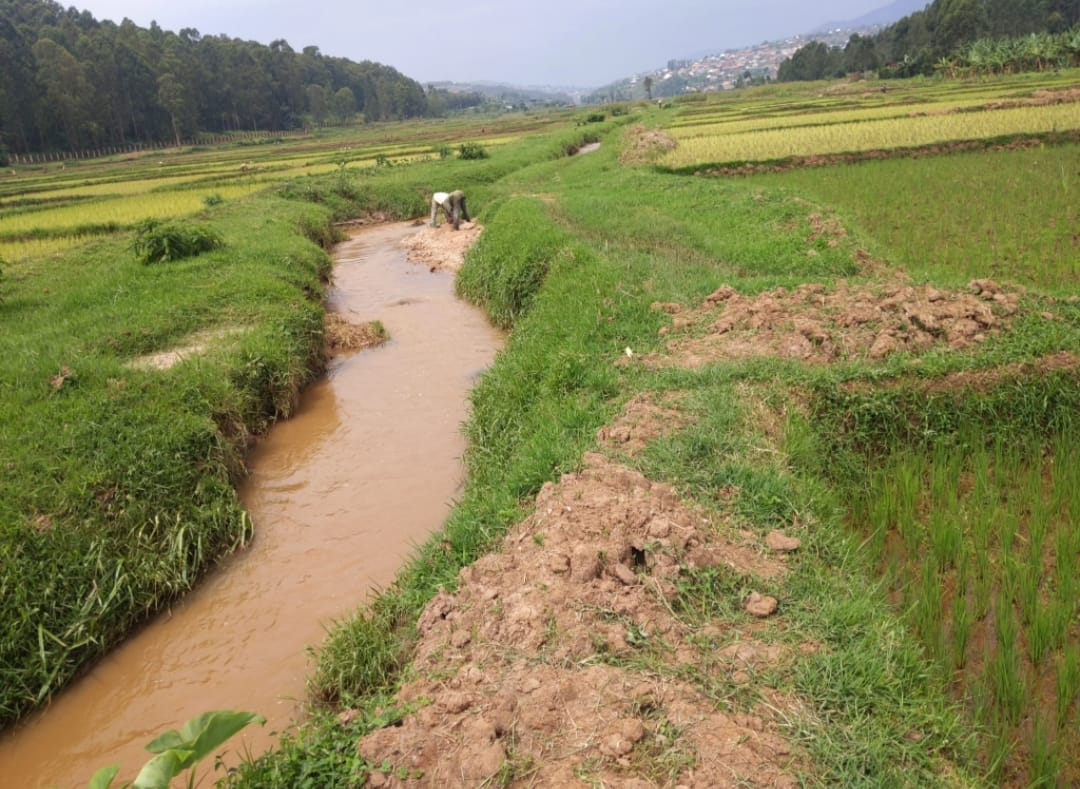
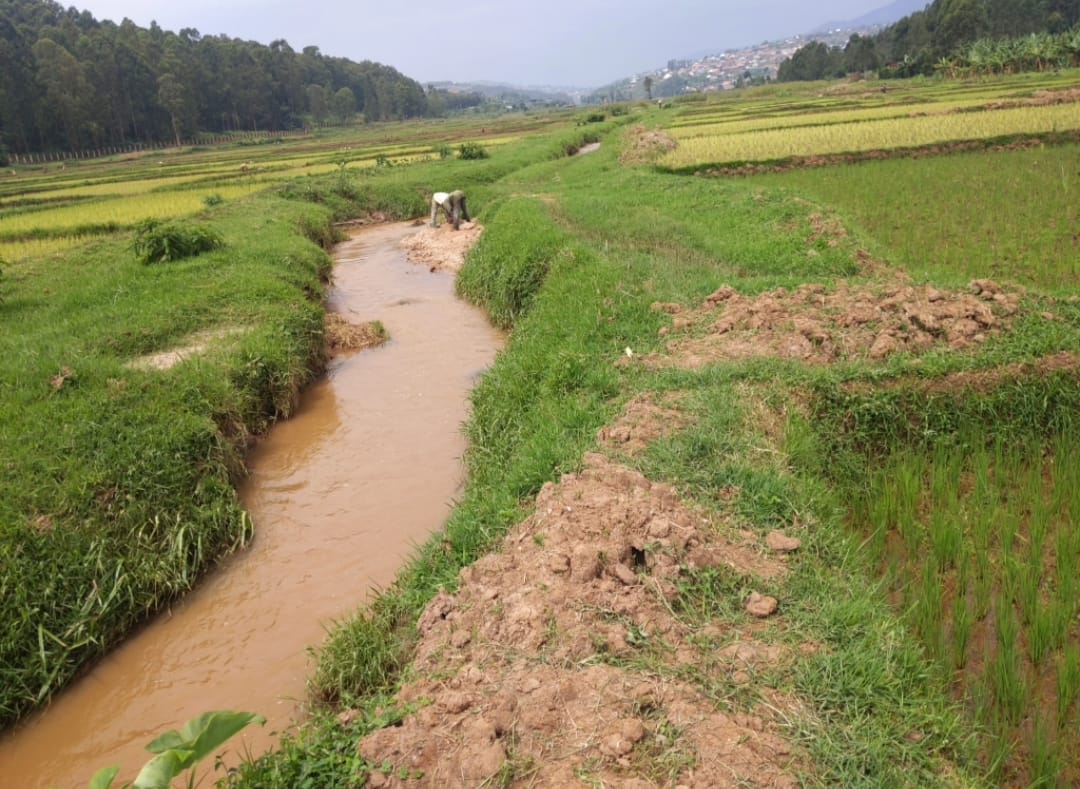
Across Rwanda, rivers like Rwasave Ndobogo in Huye District and Giciye in Ngororero District are losing water. These rivers, which were once very important, are now becoming dry this is leaving communities in need of help.
Farmers Are Losing Their Crops
Mukakarera Christine, a farmer from Huye District, says, “The Rwasave Ndobogo River used to be full of water. We could use it for irrigation, and it was home of to many fishes. But now, it’s getting smaller wich could lead to dry up, our crops are struggling. During the dry season, things get even worse.”
Farmers rely on rivers to water their crops. Without enough water, their fields dry out, leading to poor harvests and food shortages.
Fishermen Are Losing Their Livelihoods
Fishermen are also affected. Emmanuel, a fisherman from Ngororero District, says, “We used to catch plenty of fish in the Giciye River. But now, the river is shallow, and fish are disappearing. Many people in our community depend on fishing for food and income. But after they started removing sand from the river, we could no longer find fish,without fish, many families struggle to make a living, this problem is not just about losing food it’s about losing a way of life that has existed for generations.”

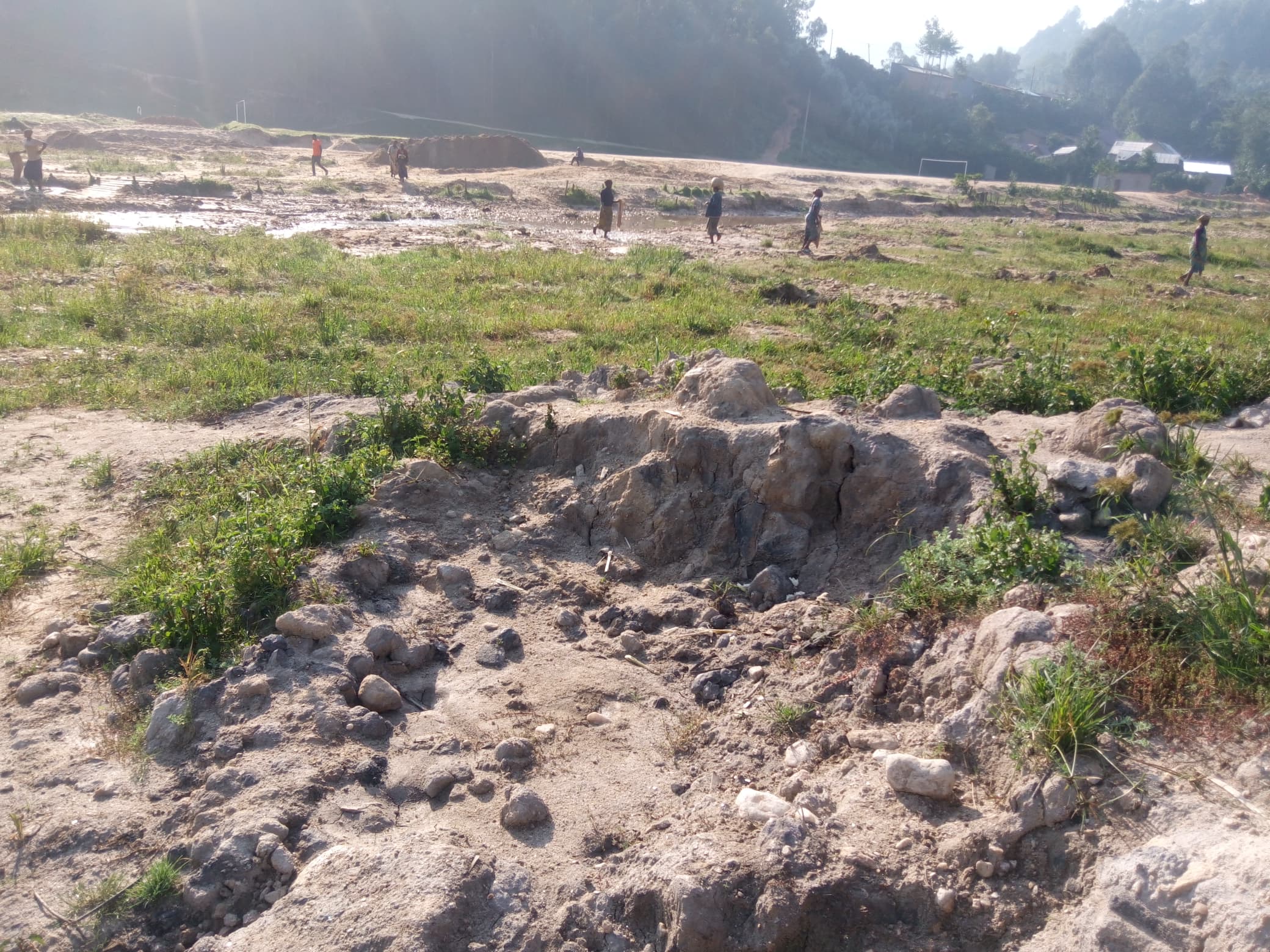
What’s Causing Rwanda’s Rivers to Dry Up?
Environmental experts say several factors are contributing to the crisis, including climate change, deforestation, sand mining, and poor waste management.
1. Climate Change and Unpredictable Weather
One of the biggest reasons behind drying rivers is climate change. Rwanda, like many other countries, is experiencing extreme weather changes. Rainfall patterns are no longer reliable. The dry seasons are getting longer, and the rainy seasons are becoming shorter and more unpredictable. This means that rivers do not receive enough water to stay full.
“Due to environmental destruction, rainfall patterns have changed,” says MP Jean Claude Ntezimana, a member of a party that fights for environmental protection (Democratic of Green Party Rwanda) “Less rainfall means less water flowing into our rivers, and higher temperatures cause more water to evaporate, .”
The MP also warns that when rivers dry up, fish and other aquatic animals die. “Rivers and forests help regulate the climate. They produce the moisture needed for rain, When a river is polluted, the air quality worsens, leading to diseases such as skin cancer and respiratory illnesses. But now, because of human activities, the rainfall pattern has changed. For example, February is usually not a hot month in Rwanda, but this year, we experienced extreme heat, This shows that things are not as they used to be before the environment was destroyed.”
The Rwanda Meteorology Agency (Meteo Rwanda) has announced that temperatures have increased significantly in recent years, especially in 2024. The temperature has risen by 1.55 degrees Celsius, while in previous years; it only increased by up to 0.8 degrees Celsius. This rise has made people feel the heat more, even inside their homes at night.
In September 2024, temperatures in Rwanda ranged between 20 and 32 degrees Celsius. This level of heat was not very common before. Nyagatare District often experiences the highest temperatures. For example, on January 14, after midday, the temperature in Nyagatare reached 31 degrees Celsius.
2. Deforestation
Trees play an important role in keeping rivers healthy. Their roots hold the soil together, preventing erosion and allowing water to flow smoothly. However, deforestation has increased in Rwanda as trees are cut down for firewood, farming, and construction.
Without trees, the soil washes into rivers, making them shallow. Over time, this leads to rivers disappearing.
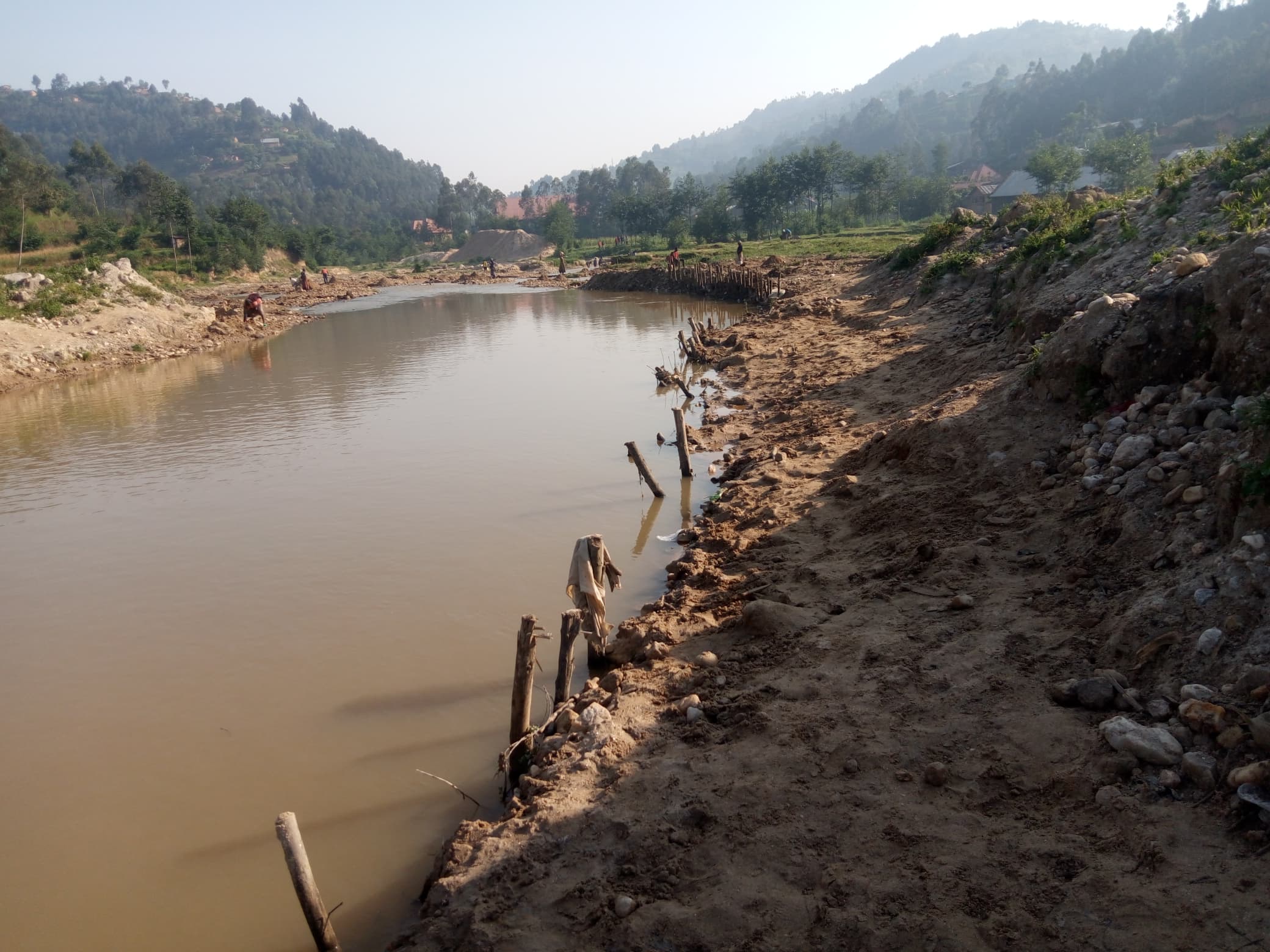

“This is a serious problem,” explained by MP Jean Claude Ntezimana. “Our party has been researching this issue for a long time. We found that rivers are being misused and harmed by human activities. For example, we found that many people living near the Nyabarongo River use it irresponsibly. The water which comes from sand-mining areas, near garages, is highly polluted. Mechanics dump old metal parts and used motor oil into the river. Illegal mining activities also contribute to pollution. Some miners wash minerals in the river, releasing mud and sand into the water. Waste from households also pollutes the river. As a result, the river water looks dirty. We took photos and presented our findings. The Mayor of Kigali responded, saying that they would take action to stop those harming the river.” Says MP Jean Claude Ntezimana, from the party that fights for environmental protection.
3. Sand Mining A Hidden Threat
Another major issue is sand mining. Sand is taken from riverbeds to be used in construction, but this weakens the river’s natural flow. When too much sand is removed, the river loses its ability to hold water, causing it to get smaller in different time.
“In some areas, sand mining is happening at an unsustainable rate,” says the Mayor of Ngororero District. “We have set stricter regulations to control this activity, and we are educating residents on how to protect the rivers which are nearby them.”
4. Poor Waste Management, Pollution: Poisoning Rivers
Pollution is another major reason why rivers are drying up. Many rivers in Rwanda are filled with waste, including plastic, industrial chemicals, and household garbage. This pollution makes the water unsafe to drink and kills fish and other aquatic life. Over time, waste buildup can block water flow, making rivers even more vulnerable to drying up.

Olivier Bizimungu, who collects scrap metal in Nyarugenge nearby Nyabarongo River, believes people need to rethink waste disposal. “Everyone knows old metal and other waste materials harm rivers, instead of polluting the water, people should sell these materials because they can still be useful.”

He added that the biggest challenge is that many people do not yet understand that old items, whether metal, electronics waste or plastic, can be sold and reused in different industries. Communities must be educated about recycling and waste management. Companies and industries should be held accountable for polluting rivers.
Additionally MP Ntezimana emphasizes the urgency of the situation: “Our Rivers are in bad condition. The Nyabarongo River, which covers almost two-thirds of Rwanda, is severely polluted. If we don’t protect our rivers, we are putting our future at risk.”
He urges citizens to take responsibility: “Protecting Rivers means protecting life both human life and the animals that depend on water. Without clean rivers, we have no future everyone must take responsibility.”

We reached out to several environmental officials (REMA) and those who are responsible for water resources (RWB) to get their views on the issue of rivers which are getting smaller in Rwanda. However, they have not commented on the matter yet. If they release any statements, we will publish them.
The communication officer at REMA told us that there is no data currently being collected on the state of the rivers.
By Hadjara Nshimiyimana.



